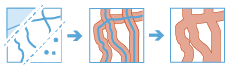
Create Buffers
A buffer is an area that covers a given distance from a point, line, or area feature.
Buffers are typically used to create areas that can be further analyzed using other tools. For example, if the question is What buildings are within 1 mile of the school?, the answer can be found by creating a 1-mile buffer around the school and overlaying the buffer with the layer containing building footprints. The end result is a layer of those buildings within 1 mile of the school.
Choose layer to apply buffer to
The point, line, or area features to be buffered. The input layers must be in a projected coordinate system or the processing spatial reference must be set to a projected coordinate system using the Analysis Environments.
In addition to choosing a layer from your map, you can choose Choose Analysis Layer at the bottom of the drop-down list to browse to your contents for a big data file share dataset or feature layer.
Select the type of buffer to apply
There are three ways you can specify the size of the buffer for your input features:
- Specify a distance that is applied to all features.
- Specify a field on the input layer that contains the distance value. You can use a string field or a numeric field. If a linear unit is not defined, the units of the spatial reference will be used. If you are using a geographic coordinate system, the unitless field will be assumed to be meters.
- Build an expression with multiple fields and mathematical operators. For example, to buffer by 10 times the value of a field named wind_speed add the expression $feature["wind_speed"] x 10.
Select the buffer method
You can choose to use a Planar method or a Geodesic method. The Planar method may be faster and is appropriate for local analysis on projected data. The Geodesic method is appropriate for large areas and any geographic coordinate system.
Select the type of dissolve method
Options to specify the dissolve method. If a dissolve method is chosen, you will be given the option of creating multipart or single-part areas and you will be able to calculate statistics based on the fields provided.
- All—All features will be dissolved. If multipart features are allowed, all features will be dissolved into a single feature. If multipart is not allowed, features that are adjacent or overlapping will be dissolved.
- Fields—Features that share the same specified field or specified field combination will be dissolved. If multipart features are allowed, all features with the same field will be dissolved into a single feature. If multipart is not allowed, features that are adjacent or overlapping with the same field value will be dissolved.
- None—No features will be dissolved. This is the default.
Allow multipart features
Option to specify if your result will consist of single-part or multipart features.
- Checked—The results of your analysis will be contain multipart features.
- Unchecked—The results of your analysis will contain single-part features, This is the default.
Add statistics (optional)
You can calculate statistics on features that are summarized. You can calculate the following on numeric fields:
- Count—Calculates the number of nonnull values. It can be used on numeric fields or strings. The count of [null, 0, 2] is 2.
- Sum—The sum of numeric values in a field. The sum of [null, null, 3] is 3.
- Mean—The mean of numeric values. The mean of [0, 2, null] is 1.
- Min—The minimum value of a numeric field. The minimum of [0, 2, null] is 0.
- Max—The maximum value of a numeric field. The maximum value of [0, 2, null] is 2.
- Range—The range of a numeric field. This is calculated as the minimum values subtracted from the maximum value. The range of [0, null, 1] is 1. The range of [null, 4] is 0.
- Variance—The variance of a numeric field in a track. The variance of [1] is null. The variance of [null, 1,0,1,1] is 0.25.
- Standard deviation—The standard deviation of a numeric field. The standard deviation of [1] is null. The standard deviation of [null, 1,0,1,1] is 0.5.
You can calculate the following on string fields:
- Count—The number of nonnull strings.
- Any—This statistic is a random sample of a string value in the specified field.
Choose an ArcGIS Data Store to save results to
GeoAnalytics results are stored to an data store and exposed as a feature layer in Portal for ArcGIS. In most cases, results should be stored to the spatiotemporal data store and this is the default. In some cases, saving results to the relational data store is a good option. The following are reasons why you may want to store results to the relational data store:
- You can use results in portal-to-portal collaboration.
- You can enable sync capabilities with your results.
You should not use the relational data store if you expect your GeoAnalytics results to increase and need to take advantage of the spatiotemporal big data store's capabilities to handle large amounts of data.
Result layer name
The name of the layer that will be created. If you are writing to an ArcGIS Data Store, your results will be saved in My Content and added to the map. If you are writing to a big data file share, your results will be stored in the big data file share and added to its manifest. It will not be added to the map. The default name is based on the tool name and the input layer name. If the layer already exists, the tool will fail.
When writing to ArcGIS Data Store (relational or spatiotemporal big data store) using the Save result in drop-down box, you can specify the name of a folder in My Content where the result will be saved.